Meta-analysis:
- Global validity[aggregate of individual variables] (predictive/criterion validity) of both R-PAS` and MMPI/MMPI-2 have been studied and show moderate effect sizes from .21 to .33, .29 to .33 for R-PAS; Meyer, Finn et.al.] based on 241 studies, 69 meta-analysesThese are comparable or higher than many medical tests and interventions (Meyer, Finn et.al.) e.g., EKG’s, mammograms, MRI’s, Ultrasound, PET scans (Meyer , Finn et. al p 135) Meyer and Archer (2001): From Parker et. al. ‘s meta-analysis (Parker, Hanson, and Hunsley, 1988): Validity coefficients are statistically significant and of a medium magnitude for the Rorschach (range = .27-.30), the MMPI (range = .23-.28), and the WAIS (range = .32-36).
These effects are about the same size as those found for the effectiveness of psychological, educational, and behavioral treatments, or the extent to which therapists and clients agree on treatment-related variables
“…the Rorschach, MMPI, and WAIS all have positive and meaningful evidence of construct validity regardless of predictor scales, criterion variables, target populations, literature sampling strategies, or determinations about what constitutes a meaningful hypothesized effect. (Meyer and Archer, 2001)
- Positive predictive power of R-PAS, MMPI/MMPI-2, Millon (1,2,3,4) tests: are all moderate and comparable to EKG’s, mammograms, MRI’s, Ultrasound, PET scans (Meyer , Finn et. al p 135)
- Ganellen (2013) MMPI and Rorschach, according to multiple meta-analytic reviews in the literature: comparable in terms of reliability, test-retest stability, validity
- R-PAS: The concept of error rate does not apply very well to personality assessment, where “goodness of fit” is a better criterion than “known error rate.”
However, most of those R-PAS variables that are susceptible to use in classifications and predictions have been tested against reasonable criteria in a manner from which approximate error rates can be derived. An estimate of the average error rate for most of R-PAS can be derived from Mihura et al.’s(2012) meta-analytic data, which found an
overall effect size for adults as measured against diagnostic and behavioral criteria of about 0.30, which (using binomial conversion) falls squarely within the typical range of variable-to-criterion error rates found in personality testing (Hemphill,2003) of approximately 0.30 Reliability studies: 1) Test-retest; 2) split-half; 3) inter-raterMMPI-2, MMPI-2 RF and MCMI are highly reliable: internal consistency, temporal stability over short and medium and long term (Graham , 2012) - MMPI: e.g. Telegen and Ben-Porath – Test-retest higher order .71-.91, F,L,K over .7 in normal population, RC scales (from .63 for RC6, rest >.74)
- Comparable to MMPI-2 studies (Ganellen)
- MMPI-2 RF: Test-retest .80-.90 range for higher-order scales; .64 (RC6-.89 for RC4). Internal consistency for higher-order scales .80’s to .90’s; RC scales also in .80’s to .90’s; PSY-5 .69-.77
- Tellegen and Ben-Porath, more than 50k correlations between MMPI-2 RF scales and external criteria è convergent and discriminant validity for all higher-order scales.
- A sizable literature on the RC scales (also in the MMPI-2) showing that the RC scales measure specific areas of functioning while reducing the effect of demoralization. Convergent validity equal to or in some cases greater than the original clinical scales (Graham)
- Empirical Correlates in nMental Health
- Outpatient
- Inpatient Medical
- Substance Abuse Treatment
- n Forensic- Civil
n Forensic- Criminal
n Non-Clinical
- Manual: Ben Porath: nN= 4,336 Men; 2,327 Women n604 Criteria
n53,886 Correlations
- n Forensic- Civil
Ben-Porath 2011 :

- Many peer reviews on forensic applications of MMPI-2 RF
- MCMI-IV:
- Groth-Marnath: 1) internal consistency >.8 for 20/26 scales (none lower than .6);
- Temporal consistency: Test-retest reliability moderate to high (depending on length; 6 months median .78; 4 years .59-.73); Personality scales are more stable than symptom scales, as expected
- Scales from MCMI-4 are highly correlated with MCMI-3 and MCMI-3 w 2; so that data on 3 and 2 are relevant to reliability and construct and predictive validity.
- Temporal stability of scales are in Grossman’s book; above .80 for personality scales
- As are also sensitivity and specificity, which are more than adequate
- MCMI: Good pos predictive power (ranging .3 to .8)
- MCMI: > 20 Factor-analytic studies have validated the constructs measured by clinical scales (Groth-Marnath)
- Studies comparing MCMI vs. related instruments (BDI, MMPI-2, STAI, SCL-90R, MMPI-2) have supported the clinical and personality scales (MCMI-III and MCMI-IV manuals)
- Relevance: real strength of Millon is in assessment of personality style and personality disorder.
- Sensitivity: what are the chances that a person with a disorder will be identified by the test as having the disorder.
- Specificity: what are the chances that a person who does not have the disorder will be corrected classified by the test as not having it.
- Positive predictive power: percentage of cases with the disorder identified by the test.
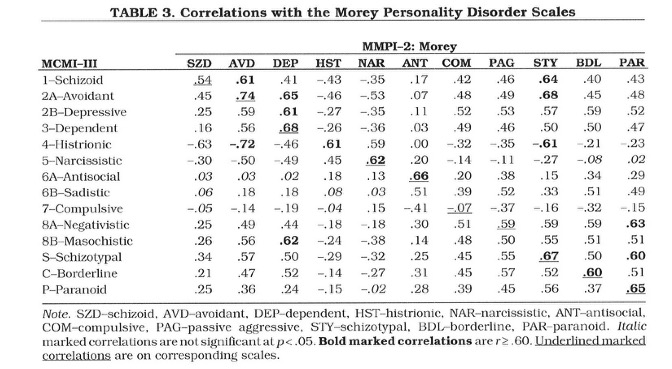
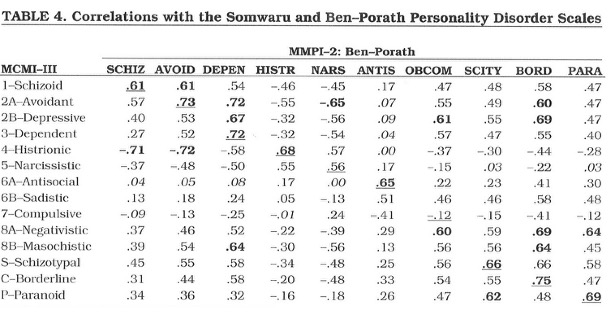
- MMPI-2/MCMI-III correlation matrix:
- Groth-Marnath: 1) internal consistency >.8 for 20/26 scales (none lower than .6);